Generate a Model
Use a .dragon1 File for generating models
Suppose you need to create a model really fast, and you want to do it nice and easy, then Dragon1 has a few options for you. One of them is to generate a model using a .dragon1 file (JSON structured) and the Dragon1 Viewer application.
If you are new to models, read this page on what is a model first.
A .dragon1 file can be created quickly by hand as a text file in Notepad, and from there, it can be uploaded to the Viewer to watch it.
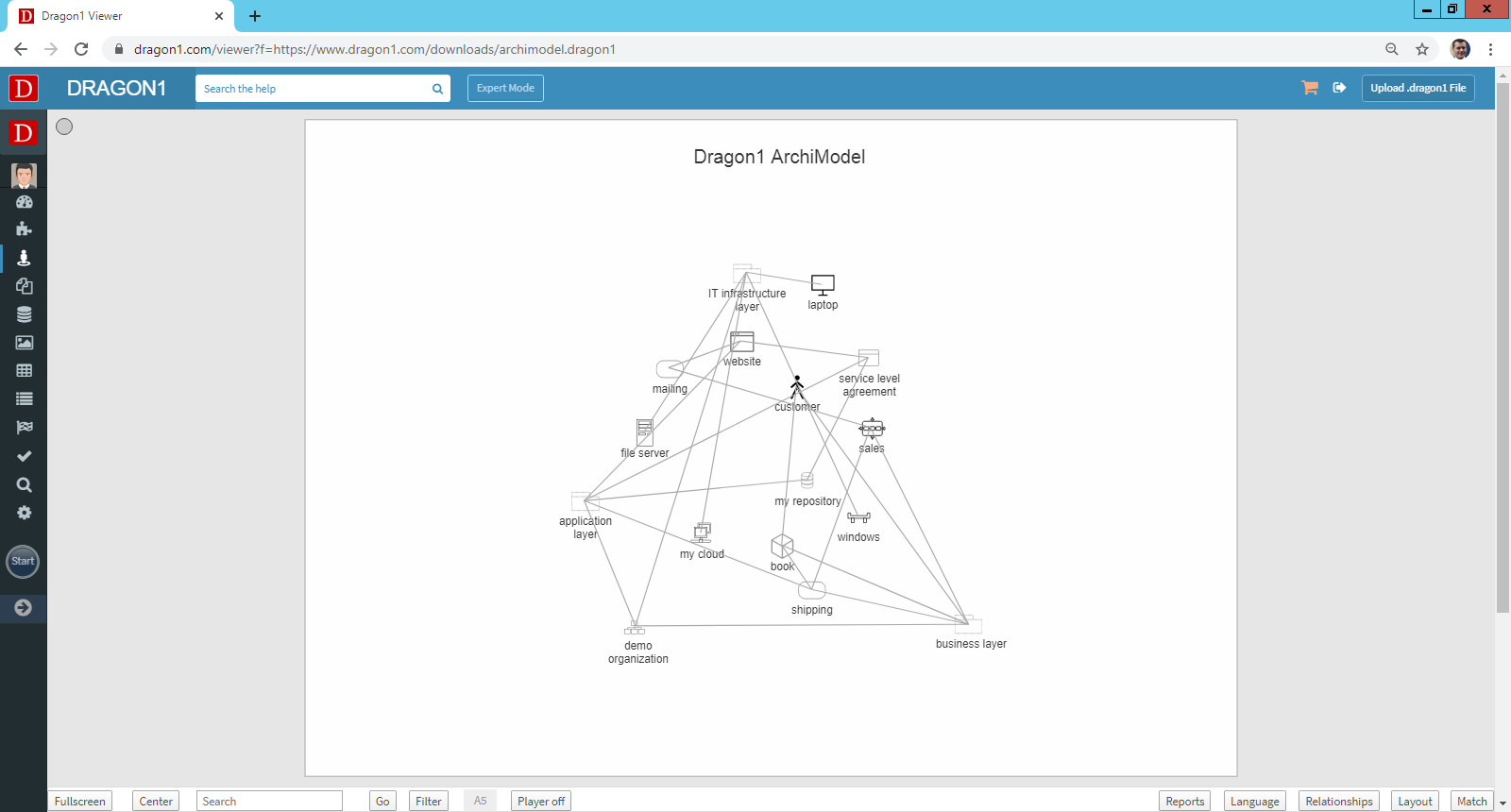
In Dragon1, many example visualizations provide a .dragon1 file containing the model's data. Those files can be downloaded and edited to fit the needs. Also, external systems can generate a .dragon1 File and use the Viewer API, as simple as providing or embedding a URL to it.
With the Dragon1 Viewer application, a model can be generated, viewed, filtered, matched, and compared with attribute values and other models, or it can be checked for compliance with other types of models.
How To Generate a Model
We have made generating a model on Dragon1 very easy.
The steps to generate a model are:
- Download an example .dragon1 File here.
- Edit the .dragon1 file in notepad. For instance, change the title and the names of the entities or add attribute values.
- Go to the Viewer
- Upload the edited file using the upload button
- You now see a forced directed graph generated from the file
- Click the canvas to stop the movement
- Drag some shapes. (Now, the X.Y positions of the shapes are generated in memory. You will see the X and Y positions if you download the .dragon1 file from the Viewer.
- Click on a shape
- Now you see the attributes of the entity you clicked.
- Click on the shape's name in the left bar. And edit the name. If you download the .dragon1 file from the Viewer, you will see the changed name in the file.
- Click the Layout button at the bottom right of the Viewer and choose the layered group layout for the model. Now, the Viewer looks for groups of data, visualizes the groups as a stack, and positions the items as part of the group inside the group.
- Edit the .dragon1 file again, set colors for some shapes, and add a rule (like explained below). Add attribute values that match or mismatch the rule.
- Upload the file and use the Report button to analyze the model.
Dragon1 allows you to create a model by hand, and it allows you to generate a model using a specialized JSON definition that you can create using any text editor. The structure of the JSON is specified on the 'What is a .dragon1 File?' page.
You can copy-and-paste the example below in a text file, then save it with a '.dragon1' extension.
[
{"class":"model","id":"1", "name":"Dragon1 ArchiModel", "language":"dragon1", "author":"Mark Paauwe", "date":"January 20, 2020", "version":"1.0"},
{"class":"organization","name":"demo organization","id":"1"},
{"class":"group","name":"business layer","id":"1"},
{"class":"group","name":"application layer","id":"2"},
{"class":"group","name":"IT infrastructure layer","id":"3"},
{"class":"actor","type":"business","name":"customer","id":"1"},
{"class":"product","type":"consumer","name":"book","id":"1"},
{"class":"service","type":"business","name":"shipping","id":"1"},
{"class":"process","type":"business","name":"sales","id":"1"},
{"class":"service","type":"application","name":"mailing","id":"2"},
{"class":"application","type":"business","name":"website","id":"1"},
{"class":"object","type":"data","name":"service level agreement","id":"1"},
{"class":"database","type":"oltp","name":"my repository","id":"1"},
{"class":"client","type":"user","name":"laptop","id":"1"},
{"class":"server","type":"file","name":"file server","id":"1"},
{"class":"platform","type":"computer","name":"windows","id":"1"},
{"class":"network","type":"public","name":"my cloud","id":"1"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"1", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"organization","sourceid":"1","targetclass":"group", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"1", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"organization","sourceid":"1","targetclass":"group", "targetid":"2", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"1", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"organization","sourceid":"1","targetclass":"group", "targetid":"3", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"1", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"group","sourceid":"1","targetclass":"actor", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"2", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"group","sourceid":"1","targetclass":"product", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"3", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"group","sourceid":"1","targetclass":"service", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"4", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"group","sourceid":"1","targetclass":"process", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"1", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"actor","sourceid":"1","targetclass":"product", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"1", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"product","sourceid":"1","targetclass":"service", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"1", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"service","sourceid":"1","targetclass":"process", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"5", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"group","sourceid":"2","targetclass":"service", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"6", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"group","sourceid":"2","targetclass":"application", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"7", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"group","sourceid":"2","targetclass":"object", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"8", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"group","sourceid":"2","targetclass":"database", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"1", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"process","sourceid":"1","targetclass":"service", "targetid":"2", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"1", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"service","sourceid":"2","targetclass":"application", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"1", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"application","sourceid":"1","targetclass":"object", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"1", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"object","sourceid":"1","targetclass":"database", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"9", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"group","sourceid":"3","targetclass":"client", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"10", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"group","sourceid":"3","targetclass":"server", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"11", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"group","sourceid":"3","targetclass":"platform", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"},
{"class":"relationship", "id":"11", "modelid":"1", "sourceclass":"group","sourceid":"3","targetclass":"network", "targetid":"1", "type":"association"}
]
Dragon1 supports 200+ entity classes. A full list of entity classes can be found on 'Overview of Entity Classes' page.
Use the Viewer
In the left menu pane, click 'Viewer', then click the 'Upload .dragon1 file' button in the top right corner. An open file dialog appears. Select your .dragon1 file and 'Open'. The file will be loaded in the Viewer. You can rearrange the entities inside the Viewer to get the desired results.
Add a Rule to the .dragon1 File
Dragon1 provides a unique feature: you can put rules in a .dragon1 File or the repository and have your model checked on these rules. Here, we only discuss rules in a .dragon1 File.
A rule definition in a .dragon1 File looks like this:
[{"class":"rule", "id":"1", "type":"security", "name":"All necessary software updates are executed", "rule-event":"onclick", "rule-condition":" application.softwareupdateversion = softwareupdate.version and application.id = softwareupdate.applicationid","action":"IF match shape.fill = 'green' ELSE shape.fill = 'red '" }]These .dragon1 File rules enable you to create a list that can check the quality of your processes and applications and the quality of the data you are using to generate and visualize the model.
Viewer API for Viewing Models
You can use the Viewer in any browser to generate and analyze a model you stored on any web server. By entering:
https://www.dragon1.com/viewer?f= and then the URL of the specific model, the model is loaded directly.
For example:
https://www.dragon1.com/viewer?f=https://www.dragon1.com/downloads/archimodel.dragon1
Create a model by hand?
If you want to learn how to create a model using the Architecture Repository, Visual Designer, or the Data Dashboard, you can go here.
Advanced Analyses Feature
The Dragon1 Viewer supports analyzing a model you are watching. This means you can match or compare it with other (reference) models or check compliance with the model regarding the rules. To do this, click the Report button and select your required report.